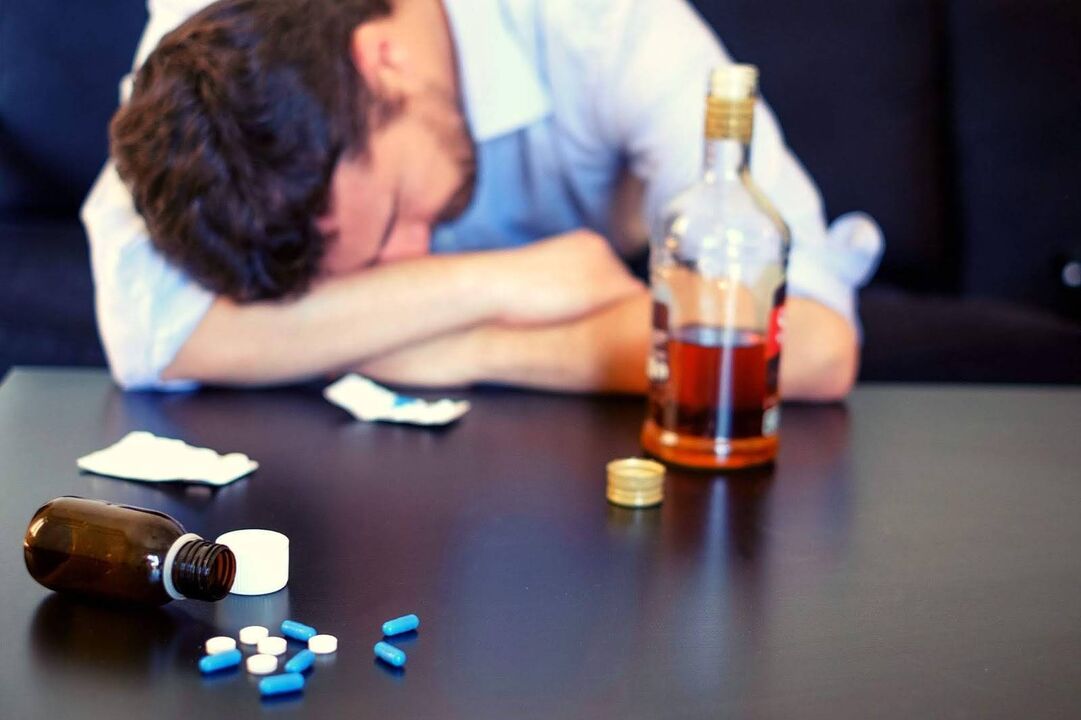
There are different opinions about the inadmissibility of the use of ethyl alcohol in the treatment of bacterial infections. Many people search the Internet for information about what is myth and what is true. People usually wonder how long it takes for the active ingredients of antibiotics to leave the body and whether they can drink alcohol after taking the last pill. Questions are often asked about the consequences of taking these 2 substances at the same time. The curiosity is linked to the reluctance of many people to enjoy a glass of wine or a bottle of beer with dinner, even when treating a bacterial infection.
What are antibiotics?
These are synthetic or natural substances that have a good antimicrobial effect. They are used in the treatment of various infectious processes, because the active components of antibacterial drugs effectively destroy pathogenic microorganisms (bactericidal) or stop their reproduction (bacteriostatic). Some drugs in this group are capable of both actions, depending on the dose taken. Indications for prescribing these drugs are bacterial infections and only a doctor can prescribe them.
The main condition for effective treatment is to strictly follow all the doctor's recommendations. During the therapeutic course, the elimination of alcohol comes first. Many people are confused by this warning. However, the course of therapy with these drugs is prescribed when the disease becomes chronic or there is a danger of developing serious complications and lasts only 5-10 days, a maximum of a week. It's not that long to give up alcohol for your health.
Why do doctors not recommend drinking alcohol during antibacterial therapy?
If a patient is being treated for a bacterial infection, doctors strongly advise against drinking alcohol. In addition, alcoholic beverages should not be consumed with any medication, as their combined use may cause disruption of somatic organs and systems. It is worth talking about several reasons that give doctors the right to prohibit patients from drinking alcohol during a course of antibiotic therapy.
Slow down the elimination of half-life products
Mentioning alcohol and antibiotics in the same phrase causes many people to think of fatal consequences in terms of acute side effects. With the simultaneous use of these 2 substances, antibacterial drugs can cause a clear disulfiram-like reaction. This reaction consists in the appearance of the following symptoms:
- colic;
- trembling;
- nausea;
- Headache;
- redness of the face;
- stomach cramps;
- confusion;
- increased sweating;
- increased heart rate;
- you feel like you can't breathe.
The appearance and intensification of such symptoms is directly related to the reaction of the antibacterial drug to ethyl alcohol. The taken pill slows down the breakdown of ethanol into safe substances, and the dangerous toxin acetaldehyde accumulates in the blood and causes severe poisoning. Therefore, experts strongly do not recommend taking a course of antibacterial therapy and continuing to drink alcohol.
It is also possible to have an incorrect treatment response. Ethyl alcohol has a retarding effect on antibiotics: they lose their activity, which leads to a decrease in their protective abilities, and the body is at the mercy of bacteria.
Increased toxicity
The use of ethyl alcohol in the treatment of infection poses a great danger to the liver. The active components of antibacterial substances can accumulate in the efferent bile ducts, blocking them, and alcohol interferes with the process of fatty acid synthesis in hepatocytes. This increased toxic effect causes liver disorders. The negative effect that occurs when drugs and alcohol-containing drinks are combined affects other vital organs. They often suffer from:
- kidneys;
- the brain;
- cardiovascular system;
- Gastrointestinal tract.
Weakening of the immune system
An immune response is necessary to overcome an infection. If they are disturbed, the disease will be prolonged. However, ethanol-containing drinks during metabolism lead to a weakening of the immune system, as a result of which recovery will have to wait a long time. In addition, the following adverse events occur:
The simultaneous use of antibiotics and alcohol leads to a decrease in the therapeutic effect and leads to the development of harmful consequences for health. Therefore, while taking a course of antibiotic therapy, you should forget to drink alcohol-containing drinks.
Ethanol contributes to the disruption of night sleep, which promotes the production of cytokines. These are special proteins that activate the immune response against pathogens. Their deficiency slows down the activity of the immune system.
Reduction of the therapeutic effect of antibacterial drugs
The liver breaks down antibiotics and ethyl alcohol using special enzymes (proteins) - acetaldehyde dehydrogenase and alcohol dehydrogenase. If you use both substances at the same time, the result will be one of two options:
Regular consumption of alcohol for several days (a condition typical of heavy drinking) causes the opposite condition. Enzymes break down the drug faster, as a result, the substance needed for recovery is reduced in the body. This slows down the healing process and in some cases even leads to the development of resistance to antibacterial agents.
When a large amount of alcohol consumed in a short time enters the body, liver enzymes begin to metabolize ethanol and the breakdown of the drug slows down. The result of this is a rapid increase in the amount of active medicinal components in the blood. This slows down the healing process and in some cases leads to increased resistance to antibacterial drugs.
The possibility of developing side effects of drugs increases
Different groups of antibiotics can cause the following side effects in some cases:
- Allergic reactions (for example, skin rash);
- Oral candidiasis;
- The appearance of dyspeptic disorders: diarrhea, nausea or vomiting;
- Occurrence of dysbiosis due to disturbance of intestinal microflora;
- Acute headache, dizziness, lack of sleep at night, daytime sleepiness;
- Cardiovascular system disorders;
- Changes in the urinary organs (infrequent or frequent urination) and musculoskeletal system (myalgia and arthralgia).
If a patient drinks alcohol during treatment for a bacterial infection, the likelihood of adverse reactions increases. This once again shows that you should not combine the use of the drug with alcoholic beverages.
How long can I drink alcohol after stopping the antibiotic?
The elimination half-life is at least 2 days after taking the drug. Moreover, if the patient has undergone a course of antibiotic therapy, this period is not enough for him. You should wait at least a week before drinking alcohol. This waiting period is necessary for the patient's body to be completely cleansed of antibiotic residues and for the patient to avoid a possible reaction - a disulfiram-like effect. According to drug groups, the waiting period is as follows:
- A person who has no chronic disease and has not received chemotherapy or radiation in the past 12 months can drink small amounts of alcohol 24 hours after finishing antibiotic therapy.
- Patients prescribed metronidazole should refrain from drinking alcohol for 2 days after the last injection or tablet.
- After finishing the course of tinidazole therapy, alcohol is prohibited for another 72 hours. Patients with a history of hepatitis or cirrhosis should avoid alcohol for at least 2 weeks after antibiotic therapy is completed.
Ethyl alcohol can be found in mouthwashes, sprays, natural herbal remedies, and dietary supplements. Therefore, the advisability of taking them during or immediately after a course of antibiotic therapy should be discussed with your doctor.
What antibacterial drugs can drink alcohol?
In-depth studies have not been conducted to confirm that the simultaneous use of ethanol and drugs that eliminate bacterial infections poses a health risk. An experiment was conducted on rats. It was done with Azithromycin, which is part of a group of antibiotics used to treat many diseases. The results of the study showed that its effectiveness does not decrease when taken together with alcohol. However, sometimes Azithromycin itself, which is quite a strong drug, can cause serious side effects, especially liver damage.
Bacteriophage. It is permissible to take this drug and alcoholic beverages together, because the effect of their simultaneous use has not been sufficiently studied. Time and accumulated statistics are needed to determine their possible interaction. However, to avoid complications, you should consult your doctor before combining Bacteriophage with alcohol.
There are a number of other drugs for the treatment of bacterial infections that do not interact negatively with alcohol. There are no contraindications directly related to ethyl alcohol in the annotations for the 5 most prescribed drugs. These include drugs that contain the following ingredients:
- Cephalexin.
- Amoxicillin.
- Ciprofloxacin.
- Azithromycin.
- Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid.
You can also take cough and cold medicines containing ethanol with these antibacterial substances. However, you should understand that alcohol in the body at the same time as the active component of antibiotics can create an increased load on all systems and cause damage to liver tissues. So, is it worth taking the risk and mixing these 2 substances?
What drugs are prohibited with alcohol?
There are several antibiotic drugs that can directly interact with ethanol. It is strictly forbidden to drink any amount of alcohol during treatment. These include drugs with the following active ingredients:
- Linezolid. The product is effective against bacteria resistant to other types of antibiotics. The drug is prescribed for skin infections.
- Fluoroquinolones. Their combination with alcohol is very dangerous due to the direct effect of the drug on the central nervous system. A patient who makes a mistake can fall into a coma.
- Aminoglycosides. These drugs are not even compatible with other drugs, especially alcohol-containing drinks.
- Cycloserine. It is used to treat lung infections and tuberculosis. Together with alcohol, it causes the appearance of convulsive syndrome.
- Lincosamides. Antibiotics from this group have a negative effect on the liver and central nervous system when taken together with alcoholic beverages.
- Tinidazole 500 mg. An antibacterial drug used to destroy single-cell pathological microorganisms. It is included in the group of drugs prescribed to relieve the patient of Helicobacteriosis.
- Metronidazole 250 mg. An antimicrobial drug used to treat vaginal and dental infections. It is added to ointments and gels used to treat bedsores and trophic ulcers.
- Cephalosporins cause severe alcohol poisoning.
Alcohol consumed during the course of treatment with these drugs causes sharp "jumps" in blood pressure. Adverse reactions occur even when the drug is administered externally.
What to do when used at the same time?
Conscious unwillingness or carelessness to listen to the doctor's advice can create a situation where antibiotics and alcohol enter the stomach at the same time. A person who commits a dangerous mixture does not immediately feel bad. If such a situation arises, it is necessary to monitor the situation. If negative reactions do not appear, you do not need to seek medical help, help yourself:
- Drink 1, 5-2 liters of a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
- Induce artificial emesis.
- Take enterosorbent (activated carbon can be finely chopped and diluted in water at the rate of 1 tablet per 10 kg of weight).
- Call your doctor and tell him that the last pill has been taken and explain why and when it happened. The doctor will decide whether the dose adjustment is necessary in a particular situation.
It is good if you can donate blood for analysis. Its results will allow us to understand whether the combination of antibacterial drugs and ethanol has a negative effect on blood parameters. However, if negative symptoms from the digestive, cardiovascular or nervous systems appear immediately after a dangerous combination, it is better to call an ambulance. This is especially true for people with a history of allergies or diabetes, as their bodies may react in unexpected ways due to increased sensitivity.
It should be remembered that the combined use of alcohol and antibiotics is very dangerous, because it creates an increased burden on somatic organs, especially the liver. You can drink a little alcohol once, because it will not cause dangerous consequences or side effects. But first, it is better to take a course of antibiotic therapy and then rest.